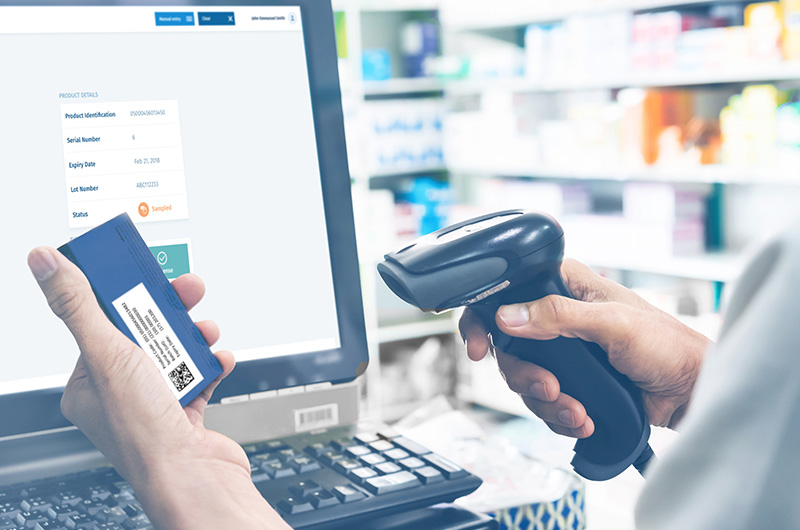
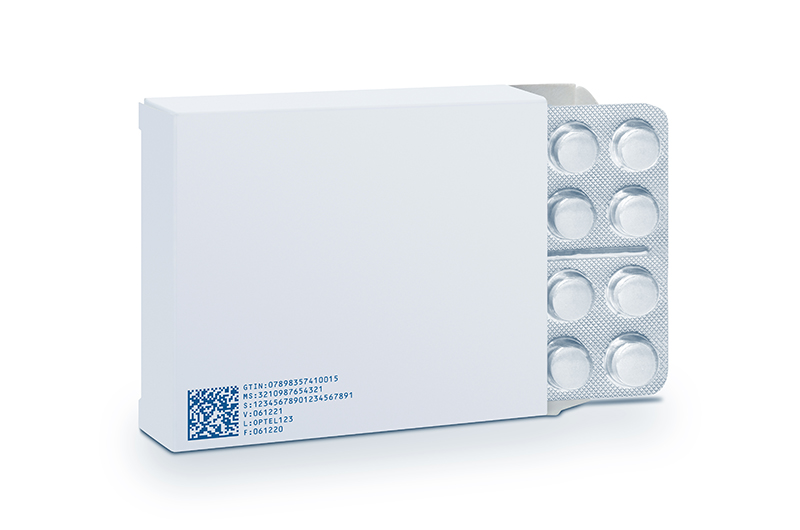
Here are some of the reasons why serialisation is necessary for the pharmaceutical industry.
HANDLING COUNTERFEIT MEDICINES
In addition to improving the supply chain, serialisation has helped to tackle counterfeit medicines. Duplicate and counterfeit medicines are raising issues with pharmaceutical companies at the global level. Manufacturers often find it difficult to stop production at a counterfeit manufacturing facility, as the medicines are manufactured in different stages and locations, and these locations can even be in different countries.
A survey by the World Health Organization revealed that almost 50% of the drugs sold on the Internet are counterfeit, and around 90% of the drugs sold are not originally from the country listed on the website.
This is where serialisation can be of great help. A comprehensive system is set up to track and trace the transit of prescription drugs. It can help identify every entity, with the help of a unique serial number. Also, it is possible to verify information such as the origin country, shelf life, and the batch number of the entity. This way, the entire life cycle of the product, right from its production, to its distribution, until it reaches the end user, is present in the database.
CHALLENGES FACED BY PHARMA MANUFACTURERS WHILE ADOPTING SERIALISATION
There’s no doubt that serialisation simplifies the business process, but it comes with a few challenges. Let’s look at the major ones:
LABEL REDESIGNING
Serialisation could mean a major change in label design for many manufacturers, to have more space for the 2D barcode. This, at times, leads to a redesigning of the graphic elements, packaging structure, etc., resulting in additional expenditure.
DATA MANAGEMENT AND AVAILABILITY
Pharma companies need to expand their data management and IT architecture to leverage the benefits of Serialisation. The IT department must be agile and sound enough to generate, capture, store, and transmit hundreds of thousands of serial numbers for different supply chains.
MAINTAINING PRODUCTION EFFICIENCY
Scanning bundles and labeling every pack will slow down the packaging process. This makes it necessary for the manufacturer to automate the process, or increase manpower, to ensure production efficiency doesn’t suffer.
COST
Introducing serialisation means updating equipment, software, and hardware, training team members, and adding more talent. All this additional cost can drive up the costs in a pharma company’s budget.
HOW DOES SERIALISATION IMPROVE THE SUPPLY CHAIN?
Irrespective of the challenges, pharma companies are adopting serialisation. Blame the mandatory guidelines or the need to become more efficient, Serialisation is becoming the cornerstone for the success of pharma companies. When executed the right way, it helps make the supply chain more transparent. At the micro level, serialisation proves to be effective against theft, counterfeiting, and diversions. Being able to trace the live location of the product also makes it easy to keep an eye on the shipment, and remove defective or recalled products, if required.
FACTORS TO CONSIDER WHEN IMPLEMENTING SERIALISATION
Switching to serialisation comes with its own set of expenses and changes. Here are some of the factors that will require your attention when you implement Serialisation to improve the supply chain:
COST
Before implementing serialisation, pharmaceutical companies need to allocate a budget to upgrade their equipment, software, and hardware to apply for serial numbers and manage the data procured during the process.
RESOURCES
Do you have enough resources and manpower to automate the entire process? As there is no standard rule book for serialisation in pharma industries, it can get a little tricky when it comes to understanding the whole concept and implementing it successfully. Companies will need resources to plan the implementation part. Also, staff training might become a necessity to ensure you are optimizing the newly introduced process to its fullest.
CHOOSING A VENDOR
Not all pharmaceutical companies will be interested in setting up an in-house serialisation department. This is where a vendor comes into the picture. Finding a vendor who brings with them extensive experience in Serialisation integration in the pharmaceutical industry is not an easy task.
AUTOMATION AND DATA MANAGEMENT
Initially, serialisation is going to impact production speed, especially in the packaging phase, the reason being the addition of serial numbers on every product, package, case package, and pallet package.
The manufacturing and packaging facility will need systems to store data generated from serialisation to give users easy and live access.
DATA EXCHANGE
The whole concept of serialisation could fail if you do not provide the data for external sharing. There must be systems in place to ensure the secure sharing of data with supply chain handlers and your direct customers.
CONCLUSION
Product serialisation and managing it is becoming the lifeline of pharma companies and supply and distribution networks. Despite the challenges it entails, serialisation is the way of streamlining the process and taking the security and reliability of pharma’s global supply chain to the next level.