The current Ecodesign Directive 2009/125/EC has been a driving force behind substantial benefits for businesses, consumers, and the environment. In 2021, the measures undertaken saved EUR 120 billion in energy costs for EU consumers, resulting in a 10% decrease in annual energy consumption for the covered product groups.
ESPR: A NEW APPROACH
The proposed Ecodesign for Sustainable Products Regulation (ESPR), introduced on March 30, 2022, represents a pivotal shift in the European Commission’s strategy toward more sustainable and circular products.
FRAMEWORK AND SCOPE
ESPR establishes a comprehensive framework for setting ecodesign requirements aimed at enhancing traceability, circularity, energy performance, and overall environmental sustainability. The regulation covers almost all categories of physical goods in the EU market, with specific exceptions such as food and feed. Noteworthy is the ability to set horizontal rules for product groups with common characteristics.
ESPR empowers the setting of diverse requirements, including those related to:
- Product durability, reusability, upgradability, and reparability
- Presence of substances inhibiting circularity
- Energy and resource efficiency
- Recycled content
- Remanufacturing and recycling
- Carbon and environmental footprints
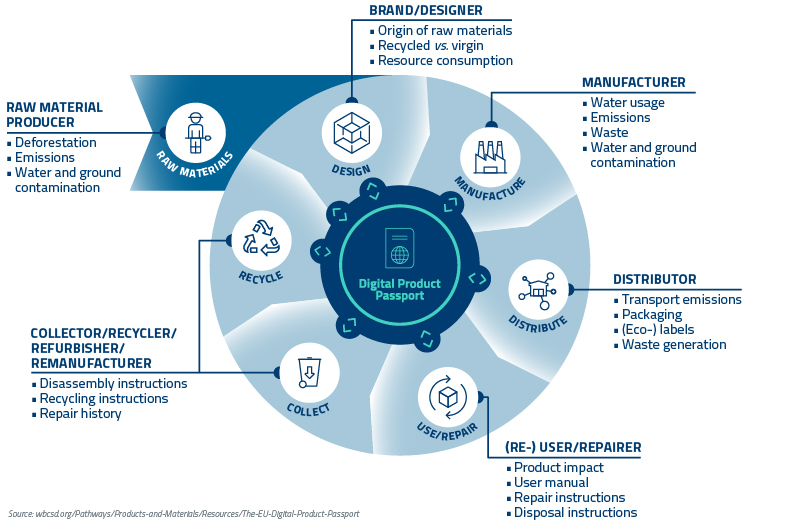
- Information requirements, including the introduction of a Digital Product Passport.